Sell more with higher margin. Exit stock with lower markdowns. Build accurate demand predictions.
Unlock success with precision by leveraging our advanced market intelligence, predictive analytics and pricing management solutions.
Aimondo fuels long-term profitable growth for 360 market leaders












































































Your All-in-One, Enterprise-Level Pricing Platform: 100% Flexibility, Zero Compromise
AI-powered platform that brings together the most accurate market intelligence, Pricing Analytics, Predictive Analytics and Pricing Management. Fine-tune all the elements to achieve your business goals faster.
Better pricing intelligence. Focused Clarity. Improved business results
Our Ai-Data & Intelligence solution empowers Sales, Marketing & BisDev teams to achieve better business results, enhanced profit margin and higher revenue by providing top quality market monitoring and competitive position analysis




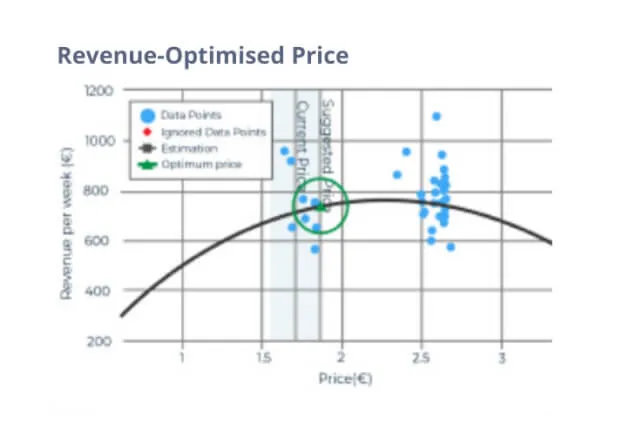

Your fastest journey from data to accurate decisions
Forecast demand. Adjust your prices. Take ultimate control of your sales velocity with the power of AI-driven predictive analytics software. Calculate price elasticity and optimise prices for relevant business goals (overstock prevention, Price Leadership, higher margin, etc.).
Seamlessly integrate with tech stack you use





Sync your major business management tool with your price optimisation activities. Aimondo integrates easily with any ERP system.
Testimonials
Pricing professionals, CFOs and Directors of Ecommerce praise Aimondo for helping them achieve incredible business results in less than 6 months.
Book a demo to experience the power of Aimondo AI-driven services
Check out solutions that will fuel your long-term profitable growth. Let us help you increase your operational efficiency today.













